OpenEBench
OpenEBench (https://openebench.bsc.es) is the ELIXIR benchmarking and technical monitoring platform for bioinformatics tools, web servers and workflows. The development of OpenEBench is led by the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC) in collaboration with partners across different European projects and Life Sciences communities.
OpenEBench as platform has the overall objectives:
- Provide guidance and infrastructure support for community-led scientific benchmarking efforts.
- Provide an observatory for software quality based on the automated monitoring of FAIR for research software metrics and indicators.
- Work towards the sustainability of the platform by adopting, integrating and promoting principles on Open Software, Open Data and Open Science.
- Adopt community-led standards, protocols and/or including the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH), ELIXIR and the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC).
Building on those objectives, OpenEBench can engage with different end-user profiles across the Life Sciences communities and beyond.
- Developers, who have a reference place to identify current challenges and relevant data sets for developing new algorithms and/or measure the impact of new developments. OpenEBench offers the possibility to developers to compare the scientific performance of their solutions with others from the community. Ultimately, it helps to improve their methods and disseminate their results thanks to publications and results spreading.
- OpenEBench assists Communities in the organization of their scientific benchmarking activities and the identification of new trends in their concrete area by providing examples of assessment metrics already in use in other communities, contributing to results dissemination and establishing good practices.
- Researchers mainly benefit from getting guidance about choosing the best resource for their research needs and be aware of the latest advancements in the area by getting information from trusted experts and staying up to date with new developments.
- Funders are able to maximize impact from projects which include the development of new software resources and/or improve the existing ones.
Architecture
As described in figure 8, OpenEBench scientific benchmarking architecture has three different levels that allow communities at different maturity stages to make use of the platform.
- Level 1 is used for the long-term storage of benchmarking events and challenges aiming at reproducibility and provenance. Level 1 makes use of the OpenEBench data model (https://github.com/inab/benchmarking-data-model), which allows organizing any relevant data used and/or generated by community-led scientific benchmarking activities. Data is bundled and deposited in services provided by facilities like B2SHARE from EUDAT, where they receive a DOI. This enabes full data provenance and reproducibility for everyone involved.
- Level 2 allows the community to use benchmarking workflows to assess participants’ performance. Those workflows compute one or more evaluation metrics given one or more reference datasets. Workflows for level 2 are organized using software container technologies (e.g. Docker or Singularity), and computational workflows managers like Nextflow. This choice facilitates the deployment and use of level 2 workflows across any computational installation compatible with such technologies.
- Level 3 goes further by getting workflows specifications from participants, and then evaluating them in terms of technical and scientific performance. At this level, the whole benchmarking experiment is performed at OpenEBench; first, the predictions are made using the software provided by the participants; then, those predictions are evaluated with the benchmarking workflows; and, finally, the results are stored and visualized in the web server.
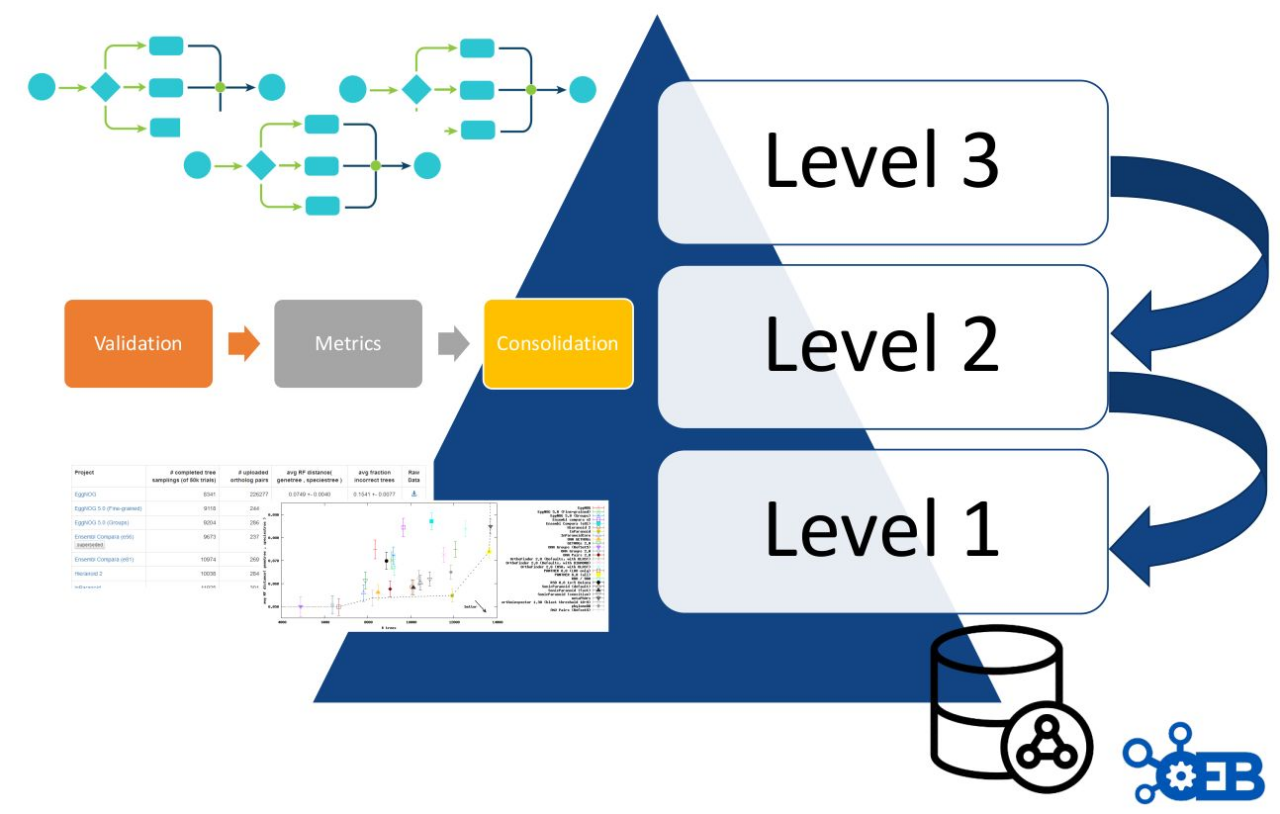
Importantly, each level makes use of the architecture defined in the previous level e.g. participants’ data generated by workflows at Level 3 are evaluated using the metrics and reference datasets in Level 2, and the resulting data is stored following the data model in Level 1 for private and/or public consumption.
EOSC Services
OpenEBench already uses ELIXIR AAI, which is intended to evolve together with other services e.g. GEANT; as Life Sciences AAI in the context of the cluster project EOSC Life. OpenEBench has started to incorporate some of EOSC Life services, specifically, WorkflowHub, as a mechanism to facilitate the provenance of the workflows used in the platform as well as a mechanism to monitor the availability and deployability of workflows used in OpenEBench within the community-led scientific benchmarking activities.
OpenEBench is integrating specific services from the EOSC Portal. Specifically, OpenEBench is integrating EUDAT services for the long-term availability of benchmarking results. To make this possible, EUDAT has created an OpenEBench Community, which will be used to associate any datasets from community-led scientific benchmarking activities. Using EUDAT allows us to assign a unique identifier, e.g. DOI, for those datasets contributed by members of communities at OpenEBench when publishing their results. In this way, it will be possible to reproduce at any time specific published benchmarking results by anyone interested. This integration requires the advanced management of users authorization as data should be deposited on behalf of their original owner rather than using OpenEBench identities.
It is expected that OpenEBench will become part of the EOSC portal portfolio by exposing and deploying the benchmarked analytical workflows as well as extending its capacity through best practices and additional services. As impact, we expect Life Science researchers will have semantically annotated, up-to-date collections of analytical workflows, which can be deployed across heterogeneous systems, organized by scientific communities around specific topics. As it is already happening, OpenEBench is contributing to organize emergent communities around scientific benchmarking activities by providing best practices and success stories of other communities.
Service Endpoint
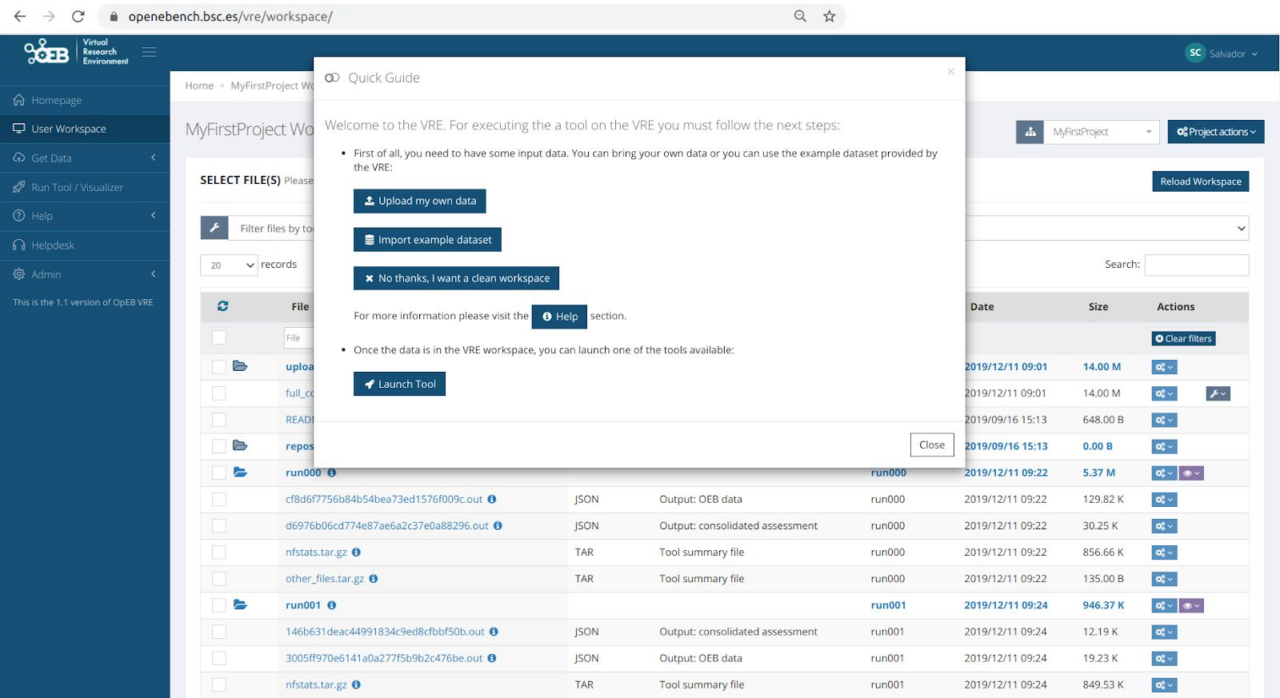
This section includes some snapshots of the interface including the access procedure. Figure (right) shows the result of a benchmark comparison, figure (left) shows the access through Life Sciences AAI and next figure shows the user’s workspace.
The service is available at https://openebench.bsc.es/. The Virtual Research Environment (VRE) is accessible at https://openebench.bsc.es/vre/tools/QFO_6/input.php?op=0. In this VRE, the users can upload their own data and applications for the execution of the benchmarks. In the general thematic service, any user can browse the information related to the benchmarks registered in the platform.
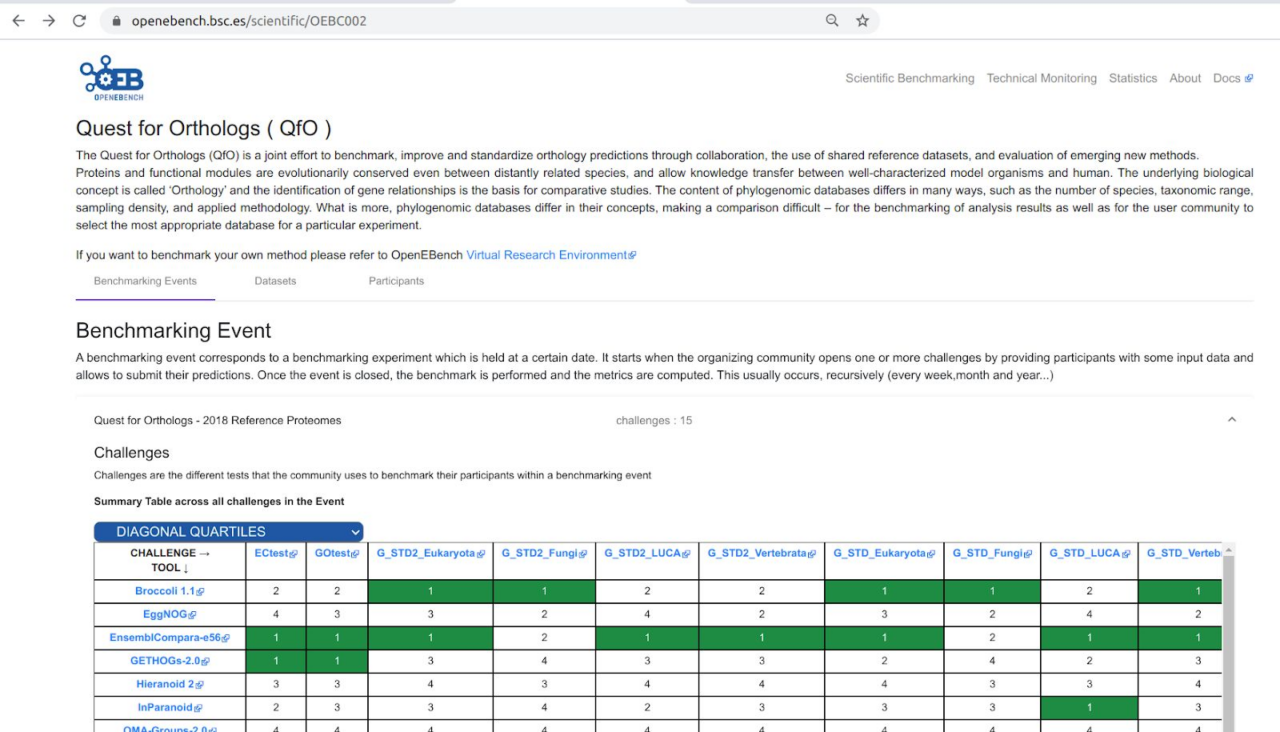
different methods for a specific benchmark using OpenEBench (right).